Bacterial cellulose-Natural polymer materials 8
Bacterial cellulose is a collective term for cellulose synthesized by microorganisms such as Acetobacter, Agrobacterium, Rhizobium, and Bacteroides.
Its typical representative is the three-dimensional nano network structure formed by β – (1 → 4) – D-glucan chains secreted by Staphylococcus aureus, which has a high crystallinity of 95%, a water holding capacity of 600%, and ultrafine three-dimensional nano fiber network characteristics.

- Feature
Bacterial cellulose and natural cellulose produced by plants or seaweed share the same molecular structural units, but bacterial cellulose fibers have many unique properties.
① Compared with plant cellulose, bacterial cellulose has no co products such as lignin, pectin, and hemicellulose, and has high crystallinity (up to 95%, compared to 65% for plant cellulose) and high polymerization degree (DP value of 2000-8000);
② Ultra fine mesh structure.
Bacterial cellulose fibers are composed of microfibers with a diameter of 3-4 nanometers combined into fiber bundles with a thickness of 40-60 nanometers, which interweave with each other to form a developed ultrafine network structure;
③ The elastic modulus of bacterial cellulose is several to ten times higher than that of general plant fibers, and its tensile strength is high;
④ Bacterial cellulose has strong water retention values (WRV).
The WRV value of undried bacterial cellulose is over 1000%, and the water holding capacity after freeze-drying still exceeds 600%.
The re swelling ability of bacterial cellulose dried at 100 ℃ in water is equivalent to that of cotton short fibers;
⑤ Bacterial cellulose has high biocompatibility, adaptability, and good biodegradability;
⑥ Controllability during bacterial cellulose biosynthesis.
⑦ Mechanical properties: Bacterial cellulose has excellent mechanical strength and elastic modulus.
⑧ Transparency and optical properties: Bacterial cellulose film has high transparency and can be used for optical devices and display materials.
⑨ Thermal stability: It has good thermal stability and can maintain a stable structure at high temperatures.
- Application areas
◊ In Biomedical Field
√ The biological safety
√ Strong water absorption performance
√ Structural controllability
(1) High end wound dressings and artificial skin
High moisture content and good breathability enable bacterial cellulose to create a moist healing environment, reducing the risk of infection, and widely used in:
♦ Burn wound repair
♦ Chronic ulcer treatment
♦ Postoperative wound management in surgery

(2) Organizational engineering scaffold materials
The nano porous structure of bacterial cellulose can simulate the extracellular matrix (ECM), supporting cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation.
Through the company’s technological accumulation in surface modification and composite processes, its cell compatibility and tissue integration performance can be further improved, making it suitable for skin, cartilage, and even vascular tissue engineering directions.
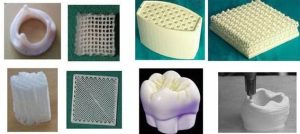
(3) Drug controlled release and active carriers
Based on the controllable structure BC material developed by Tianlu Nano, precise control of drug release kinetics can be achieved, which is suitable for:
♦ Antibacterial dressing
♦ Carrying anti-inflammatory active ingredients
♦ Vitamin and peptide delivery system
◊ In the Energy Sector
(1) Biomass energy production:
Nanocellulose is extracted from natural biomass such as lignocellulose and can be used as a key raw material for producing biomass energy.
Nanocellulose can be converted into biomass fuels such as bioethanol or biodiesel through chemical or biological conversion methods, which can be used for power generation or as a substitute for traditional fuels.
(2) Lithium batteries and supercapacitors:
Nanocellulose can be used as an electrode material or carrier for lithium batteries and supercapacitors.
The high specific surface area and conductivity of nanocellulose make it a good candidate for electrode materials, which can improve the performance and cycle life of batteries and capacitors.
(3) Solar cells:
Nanocellulose can be used to prepare flexible and transparent substrate materials for the preparation of solar cells.
Transparent conductive films based on nanocellulose can serve as substrates for flexible solar cells, providing dual advantages of mechanical strength and electrical performance.
(4) Fuel cell:
Nanocellulose and its derivatives can be used as catalyst support materials for fuel cells.
The high specific surface area and abundant functional groups of nanocellulose can effectively support precious metal catalysts, improving the catalytic efficiency and stability of fuel cells.
(5) Catalyst support materials:
Nanocellulose can be used as a supporting material for catalysts, for energy conversion and chemical reactions.
Its high specific surface area and controllable structural characteristics help to improve the activity and selectivity of catalysts, promoting efficient energy related reactions.
The application of nanocellulose has demonstrated diverse potential in the energy field, providing new material choices and innovative paths for the development of sustainable and efficient energy technologies.

◊ In papermaking field
(1) Enhance paper performance
Nanocellulose can significantly improve the mechanical strength and physical properties of paper, including tensile strength, tear strength, and flexural strength.
Adding a small amount of nanocellulose can significantly improve the strength of paper, making it more durable and tear resistant.
(2 )Improve the optical properties of paper
Nanocellulose can improve the transparency and smoothness of paper, and enhance its optical properties.
This is particularly important for high-quality printed materials such as magazines, picture books, and high-end packaging materials.
(3) Improve the barrier performance of paper
Nanocellulose can be used as a coating material for paper, significantly improving its barrier properties against moisture, oil, and gas.
This type of paper can be used for food packaging and other fields that require moisture and oil resistance.
(4)As an additive to improve pulp properties
In the pulp production process, nanocellulose can be used as an additive to improve the uniformity and water retention performance of pulp, reduce the loss of small fibers in pulp, and improve the forming quality and production efficiency of paper.
(5) Environmental performance
Nanocellulose is a natural biobased material with the advantages of being renewable and biodegradable.
Its application helps reduce reliance on traditional petrochemical based materials and lower environmental pollution during the papermaking process.
(6) Improve printing quality
The high surface area and excellent surface properties of nanocellulose can improve the adhesion and diffusion of ink on paper, enhance the color saturation and clarity of printed materials.
(7) Used for special functional paper
Nanocellulose can endow paper with special functions such as antibacterial, anti-static, conductive, and flame-retardant.
These functional papers have broad application prospects in fields such as healthcare, electronics, and construction.
In short, the application of nanocellulose in the fields of papermaking and printing can not only significantly improve the performance and quality of paper, but also bring environmental and economic benefits.
With the continuous development and maturity of nanocellulose technology, its application in the field of papermaking and printing will become increasingly widespread.

◊ In the Food Industry
(1)Food packaging:
Nanocellulose can be used as an additive in food packaging materials to improve packaging performance.
Nanocellulose based films have excellent gas barrier properties and mechanical strength, which can effectively extend the shelf life of food and provide better packaging protection.
(2)Food stabilizers and thickeners:
Nanocellulose can be used as a food stabilizer and thickener to improve the texture and taste of food.
Nanocellulose has good emulsifying and dispersing properties, which can stabilize the lotion and suspension systems, and increase the viscosity and taste of food.
For example, adding a certain concentration of nanocellulose to the ice cream formula can help maintain its original shape at room temperature and improve the viscosity and taste of the ice cream.
(3) Nutritional and health products:
Nanocellulose can be used as a carrier or embedding material for nutritional supplements.
For example, nanocellulose can be used to prepare nanoscale nutrient delivery systems, improve the bioavailability and stability of nutrients, and enhance the functionality of nutritional supplements.
(4)Food surface coating:
Nanocellulose can be used as a coating on food surfaces to enhance the texture and appearance of food.
Nanocellulose coating can improve the glossiness, waterproofness, and mechanical strength of food, while enhancing the quality and commercial value of food.
In addition, due to the absence of cellulase in the human body system, cellulose based coatings can withstand adverse conditions in the gastrointestinal tract and protect encapsulated bioactive compounds such as vitamins, fatty acids, curcumin, and probiotics.
(5) As a functional food ingredient
Cellulose, as one of the seventh largest nutrients, is an essential nutrient for maintaining human health.
It can soften intestinal substances, stimulate gastric wall peristalsis, assist defecation, and reduce cholesterol and glucose absorption in the blood.
Therefore, nanocellulose can also be used as a functional food ingredient. In the study of controlling food viscosity and glucose absorption, it was found that nanocellulose can significantly inhibit glucose diffusion, delay starch decomposition, and in a certain sense, play a role in “weight loss”.

◊ In Environmental Protection
(1) Wastewater treatment:
Nanocellulose can be used as an adsorbent and filter material for wastewater treatment.
Its high specific surface area and abundant functional groups make it have good adsorption capacity, which can effectively remove heavy metal ions, organic pollutants, and pigments from water.
Nanocellulose can also be used to construct nanocellulose based composite membranes for separating and filtering small particles and pollutants in wastewater.
(2) Soil remediation:
Nanocellulose can be used for soil remediation and the adsorption and degradation of pollutants.
The fiber structure of nanocellulose can increase soil porosity and aeration, which helps improve soil structure and water retention capacity.
Meanwhile, nanocellulose can serve as a carrier or catalyst support for adsorbing or degrading organic pollutants in soil.
(3) Environmental monitoring:
Nanocellulose can be used to prepare environmental monitoring sensors and devices.
By combining nanocellulose with functional materials, high-sensitivity and selective sensors can be constructed for detecting pollutants and harmful substances in air, water, and soil, achieving real-time monitoring and early warning.
(4) Water quality improvement:
Nanocellulose can be used as a material for improving water quality, such as preparing ecological filter media or plant root system simulators.
Nanocellulose has good biocompatibility and biodegradability, which can improve the ecological structure of water bodies and purify water quality.
(5) Air purification:
Nanocellulose can be used for air filtration and purification, capturing and removing particulate matter, organic gases, and volatile organic compounds from the air. Nanocellulose based filter media has efficient filtration performance and sustainable regenerability, which helps improve indoor and industrial air quality emissions.
The application of nanocellulose provides new technologies and strategies for environmental protection, which can effectively purify water and air, improve soil quality, degrade pollutants, and promote sustainable development and resource utilization.

◊ In the Textile Industry
(1) Preparation of functional textiles:
Combining nanocellulose with textile fibers or fabrics can endow textiles with specific functionality.
For example, adding nanocellulose can enhance the antibacterial, deodorizing, sunscreen, or anti-static properties of textiles, thereby improving their comfort and hygiene.
(2) Clothing reinforcement materials:
Nanocellulose can be used as a reinforcing agent to enhance the mechanical properties and durability of clothing.
Combining nanocellulose with clothing can improve the strength, wear resistance, and tensile strength of textiles.
(3) Degradable textiles:
By utilizing the biodegradability of nanocellulose, biodegradable textiles can be prepared.
These textiles can naturally degrade at the end of their service life, reducing pollution and impact on the environment.
(4) Smart textiles:
Nanocellulose can be used to prepare smart textiles, such as sensing textiles or wearable devices.
By integrating nanocellulose and functional materials, the multifunctionality and intelligence of textiles can be achieved.
◊ In the field of construction
(1) Cement reinforcement agent:
Nanocellulose can be used as a reinforcing agent for cement and concrete.
Adding nanocellulose can improve the crack resistance and strength of concrete, as well as enhance its durability and mechanical properties.
(2) Thermal insulation and insulation materials:
Nanocellulose has excellent thermal insulation properties and can be used to prepare efficient insulation and thermal insulation materials.
These materials can be applied to parts such as walls, roofs, and floors to improve the energy efficiency performance of buildings.
(3) Environmentally friendly coatings:
Nanocellulose can be used to prepare environmentally friendly coatings for wall and roof coating.
These coatings have good weather resistance and stain resistance, while reducing the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which is beneficial for improving indoor air quality.
(4) Nanocellulose based sound insulation material:
Nanocellulose can be used to prepare sound insulation materials and improve the sound insulation effect inside buildings.
These materials can reduce noise transmission, improve indoor comfort and privacy.
◊ In the Field of Automotive Manufacturing
(1) Lightweight materials:
Due to its high strength, low density, and excellent mechanical properties, adding nanocellulose to plastics, resins, and composite materials for manufacturing automotive components such as body and interior can reduce vehicle weight, improve fuel efficiency and performance.
(2) Reinforcing materials:
Nanocellulose can be combined with other materials to form nanocomposites, which are used to enhance the strength, stiffness, and durability of automotive components.
These composite materials can be applied to body frames, engine hoods, doors, seats, and other parts to improve the overall structural performance of automobiles.
(3) Flame retardancy and high temperature resistance:
Nanocellulose has excellent flame retardant properties and high temperature resistance, and can be used to manufacture automotive interior components such as seat fillers, insulation materials, and engine parts, improving the safety and durability of automobiles.
(4) Environmental Protection and Renewable Energy:
Nanocellulose typically comes from natural cellulose materials such as lignocellulose or plant fibers, and has the characteristics of being renewable and environmentally friendly.
In automobile manufacturing, the use of nanocellulose can reduce dependence on traditional plastics and synthetic materials, reduce the consumption of non renewable resources, and meet the requirements of sustainable development.
(5) Other applications:
Nanocellulose can also be used to improve the air filtration system, sound insulation materials, and interior fabrics of automobiles, enhancing the comfort and air quality inside the car.
In addition, adding nanocellulose can improve the performance characteristics of materials, such as increasing their impact resistance, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, thereby extending the service life of automotive components and reducing maintenance costs.
Overall, nanocellulose, as an advanced functional material, has broad application potential in the field of automotive construction.
It can help manufacturers reduce costs, improve performance, enhance safety, and promote the development of the automotive manufacturing industry towards environmental protection and sustainable development.

- Prospects and Challenges
- Production cost: The cost of large-scale production of bacterial cellulose is relatively high, requiring optimization of cultivation conditions and improvement of production efficiency.
2. Yield and purity control: More effective cultivation and purification methods need to be developed to ensure high yield and purity.
3. Application development: Further research and development are needed to explore the specific applications of bacterial cellulose in different fields and broaden its application scope.
In summary, bacterial cellulose has become a hot topic in scientific research and industrial applications due to its unique properties and wide application potential.
With the continuous advancement of technology, its application fields will continue to expand.
Are you looking for Bacterial cellulose? Welcome to contact us.
PRIME CHEMICALS are experienced in polymers, chemicals and modified plastic materials for more than 23 years. If there is any inquiry, welcome to contact us and Whatsapp: 0086 13817820852.