Calcium fluoride-Essence of Industrial Production
Calcium fluoride is an inorganic fluoride with the chemical.

Formula CaF₂
Molecular weight: 78.07
CAS: 7789-75-5
Melting point: 1423°C
Boiling point: 2497°C
Density: 3.18 g/cm³
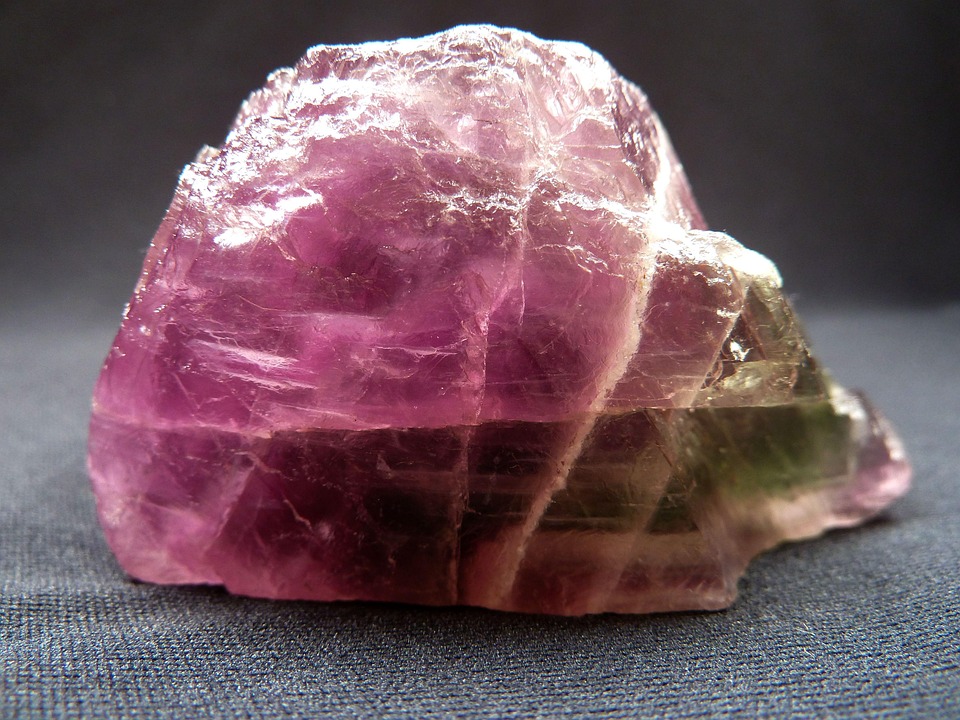
Calcium fluoride is typically an odorless crystalline or white powder.
Its natural mineral form is also known as fluorite or fluorspar, and due to impurities, it may exhibit slight green or purple hues.
It is extremely insoluble in water but soluble in hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and ammonium salt solutions, while insoluble in acetone.
It forms complexes when dissolved in aluminum or iron salt solutions.
It reacts with hot concentrated sulfuric acid to form hydrofluoric acid.
It can form eutectic mixtures with various metal oxides and emits light when heated.
Calcium fluoride has a wide range of applications, and with the advancement of science and technology, its prospects for use are becoming increasingly broad.
Primarily used in semiconductor manufacturing,metallurgy, chemical industry, light industry, optics, engraving, and national defense industries.
- In semiconductor manufacturing, ultraviolet-grade calcium fluoride single crystals serve as core components of 193nm deep-ultraviolet lithography machine lenses, directly impacting the precision of chip processes below 45nm.
In the infrared application field, their >94% transmittance at 5μm makes them the preferred material for infrared sensors and thermal imager protective windows.
- In the defense and military sector, it is used in laser weapon systems and reconnaissance satellite optical payloads, maintaining structural stability under high-temperature conditions.
In high-energy physics, it serves as a γ-ray scintillator in particle detectors and is also employed for window applications in synchrotron radiation beamlines.

- Calcium fluoride is widely used in metallurgical fluxes, primarily due to its core functions of lowering melting points, improving slag fluidity, desulfurization and dephosphorization, and optimizing metal properties, which significantly enhance smelting efficiency and product quality.
Specific applications and mechanisms are as follows:
√ Lower the melting point and promote slag flow
√ Desulfurization and dephosphorization to enhance metal purity
√ Optimize metallic properties and reduce burn-off
√ Composite Flux and Low-Carbon Smelting Trends

4. It has extensive applications in the chemical industry, primarily involving the production of hydrofluoric acid, catalysts, fluoride raw materials, and wastewater treatment.
5. The applications of calcium fluoride in the light industry primarily include ceramics, glass manufacturing, and cements,
6. Calcium fluoride is primarily used in glass engraving, where it achieves pattern etching through chemical reactions.

Market prospects of calcium fluoride
The market prospects of calcium fluoride are mainly concentrated in high-end fields such as optics, semiconductors, and new energy.
It is expected that the global market size will reach 119 million US dollars by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of about 5.19% -5.8%.
The following is a specific analysis:
√ Global Market Size Forecast
The global market size of calcium fluoride crystals is expected to be $119 million by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.19% from 2024 to 2030.
The optical field is the largest downstream, accounting for 37% of the market share, while semiconductors and defense industries account for 30% and 15% respectively.
√ Market share and growth in China
The scale of China’s calcium fluoride crystal market is expected to reach 11.64 million US dollars in 2023, and is projected to grow to 19.32 million US dollars by 2030, with a CAGR of 7.30%.
China is one of the world’s major producers, but high-end products still rely on imports.
√ Driving factors
Semiconductor demand: Single crystal calcium fluoride is widely used in processes below 45nm, with an annual growth rate of up to 8%.
New energy and environmental protection: The demand for green materials such as fluorinated refrigerants and fluorinated polymers is increasing.
Resource scarcity: The continuous rise in fluorite ore prices (up 12% from 2020 to 2024) has pushed up the cost of calcium fluoride.
√ Competitive landscape
The top five global manufacturers hold approximately 72.64% of the market share.
The Asia Pacific region (including China) is the largest market, accounting for 39% of the global market share.
√ Risks and Challenges
Technical barriers:
Crystal growth and doping modification technologies are concentrated in a few enterprises.
Supply chain dependence:
High purity calcium fluoride raw materials rely on fluorite ore, and resource depletion may exacerbate supply shortages.
PRIME CHEMICALS are experienced in polymers, chemicals and modified plastic materials for more than 23 years. If there is any inquiry, welcome to contact us and Whatsapp: 0086 13817820852.
#Calcium fluoride#Hydrofluoric acid#Sulfuric acid#Nitric acid#Metallurgy#Chemical industry#Light industry#Optics#Engraving#Defense industry#Catalyst#Wastewater treatment#Ceramics#Glass